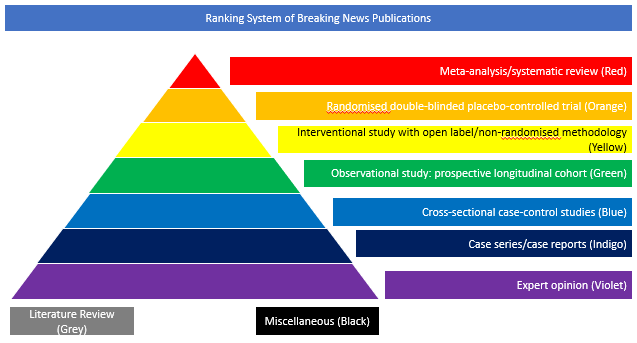
Meta-analysis Systematic Review (Red)
The objective of this study was to review the EEG findings in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 infection through a systematic review of published articles. The authors systematically searched until July 25 2020 for published articles that reported on descriptive EEG findings in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in PUBMED by Medline, EMBASE, and CENTRAL by the Cochrane Library. From a total of 94 identified records, 29 relevant articles were included in this review. A total of 177 patients with COVID-19 with descriptive EEG reports were analysed. The most common indication for EEG was unexplained altered mental status. Disturbances of background activity such as generalised and focal slowing were seen, as well as epileptiform abnormalities and rhythmic or periodic discharges. There were no consistent EEG findings specific to COVID-19 infection. The authors concluded that the EEG findings in COVID-19 appear to be non-specific. Further research on the relationship of EEG findings to the clinical state, short- or long-term prognosis of COVID-19 patients may be conducted to help clinicians discern which patients would require this procedure.
DOI: 10.1016/j.seizure.2020.09.007